Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become increasingly popular as internet users seek to protect their privacy and access restricted content. Offering a secure and private connection over the public internet, VPNs allow users to browse the web confidently.
In this article, we will explore the different VPN types, helping you to understand their purpose and choose the right one for your needs. By the end of this article, you’ll clearly understand the various VPN types and their applications, empowering you to make informed decisions in today’s digitally connected era.
Understanding VPN & VPN Types
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that allows you to establish a secure and private connection to another network over the Internet. By creating an encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server, VPNs protect your online identity and enhance your security while browsing the web.
VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, ensuring that all your communications and data transfers are secure and difficult for third parties to track or intercept. There are several types of VPNs available, each suitable for specific purposes and offering unique features.
One of the most common VPN types is the Remote Access VPN. This VPN connects users to a private network via a secure remote server. Another type of VPN is the Site-to-Site VPN, which is commonly used by businesses to connect multiple office locations securely over the internet.
To start using a VPN, you need to choose a suitable VPN service and install the necessary software on your devices. Once set up, you can simply connect to the VPN server of your choice and enjoy a secure and private browsing experience. Remember that selecting the right VPN depends on your needs, such as security, privacy, or accessibility to geo-restricted content.
VPN Types
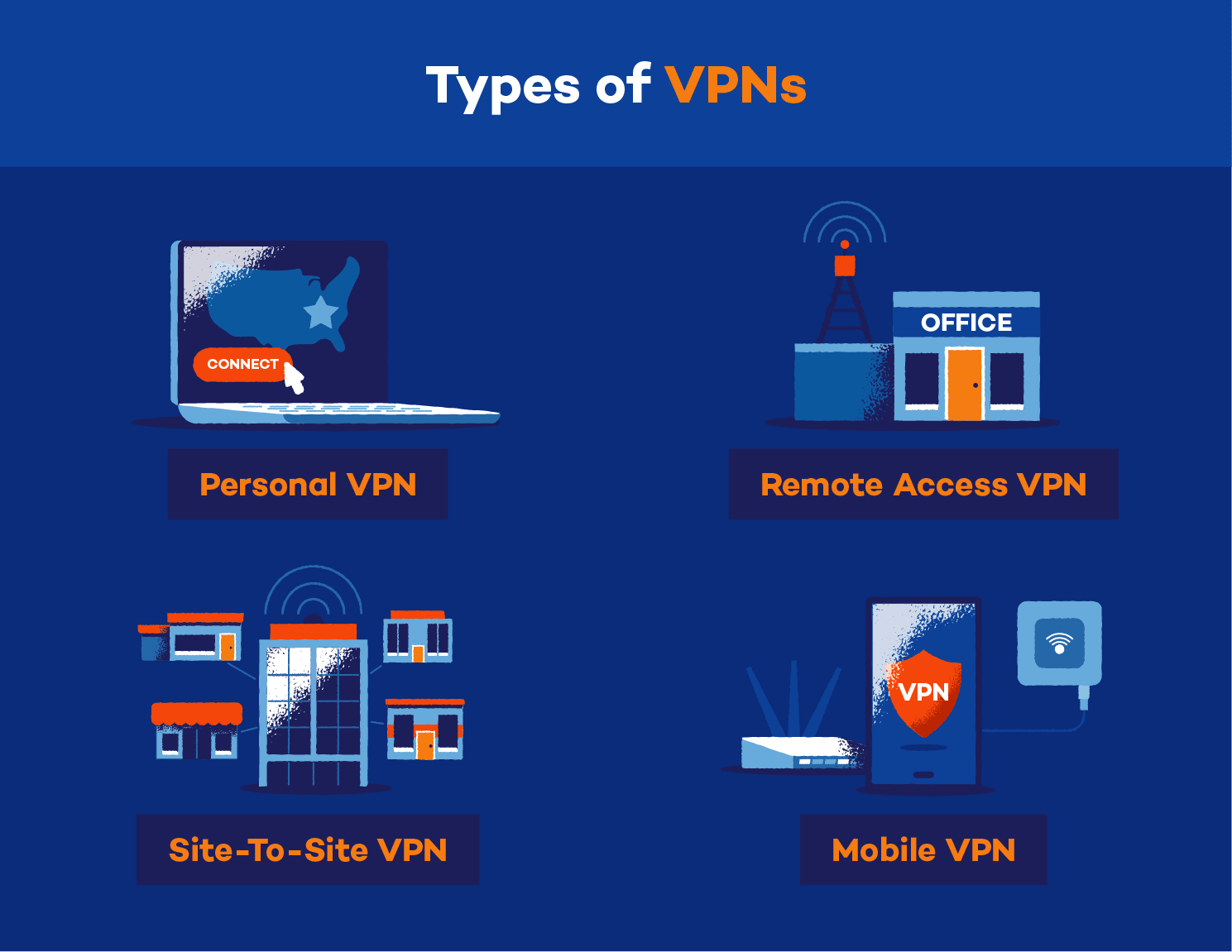
As we told you, there are four main VPN types which cater to different needs and use cases. In this section, we will explore site-to-site VPN, remote access VPN, mobile VPN, and the various VPN protocols that facilitate secure connections.
1. Site-to-Site VPN
A site-to-site VPN connects two networks securely – usually an organisation’s main office and a remote branch office. Instead of establishing single-user connections, a site-to-site VPN connects the entire network at each location. This enables staff at both sites to access shared resources without compromising security. Examples of site-to-site VPNs include IPsec and OpenVPN.
2. Remote Access VPN
When an individual needs to access a private network from a remote location, they can use a remote access VPN. This type of VPN permits users to connect to a private network and access its resources online. A secure and private connection is maintained, ensuring the user’s data remains safe from potential security breaches. Some popular remote access VPNs include SSL/TLS VPNs and Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) VPNs.
3. Mobile VPN
With the increasing use of smartphones and tablets, mobile VPNs have gained popularity. These VPNs are specifically designed for mobile devices, ensuring uninterrupted and secure access to private networks even when moving between different networks or switching between Wi-Fi and mobile data. Mobile VPNs often use Internet Key Exchange v2 (IKEv2) and Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) as their preferred protocols.
4. Personal VPN
A personal VPN is a service that creates a private and encrypted connection over the internet, allowing users to securely transmit data and maintain privacy by masking their IP address and location. By routing the user’s internet traffic through a secure server, the VPN helps protect the data from being intercepted, ensures online anonymity, and can also be used to access content that might be restricted or censored in certain regions.
VPN Protocols
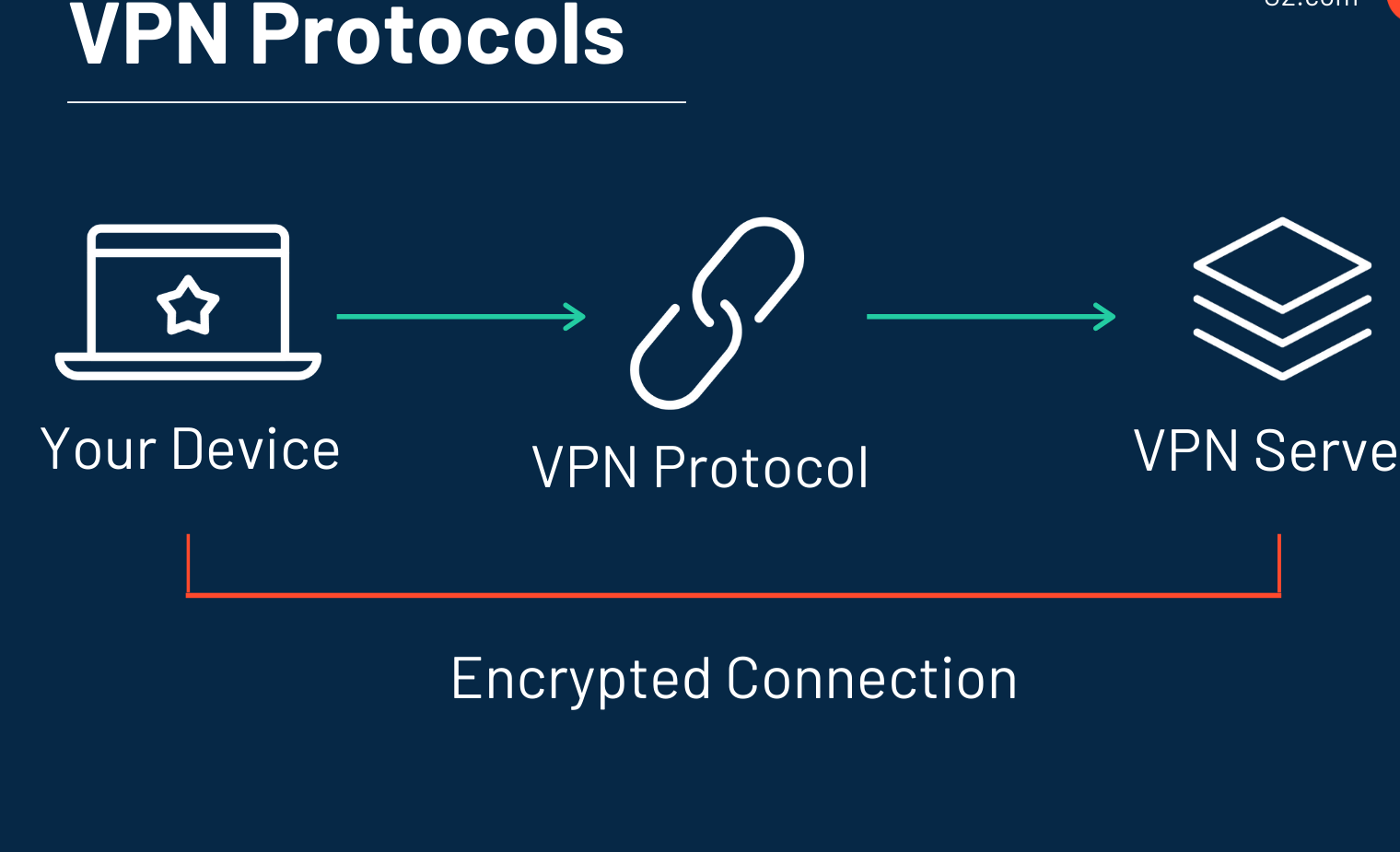
VPN protocols decide how the data is transmitted and secured between your device and the VPN server. There are various VPN protocols that offer differing levels of security and features. In this section, we will explore some of the leading VPN protocols.
- IPSec: Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a popular protocol to secure communications over IP networks. It uses a combination of authentication and encryption to protect data in transit. With its strong security features, it is well-suited for site-to-site or remote access VPN connections.
- PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is less secure than other options. It is fast and easy to set up, making it suitable for personal VPNs where high security is not a priority.
- L2TP: Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is often combined with IPSec to provide an extra layer of encryption. L2TP does not provide encryption, so it is used with IPSec to create a secure VPN connection.
- OpenVPN: A popular open-source VPN protocol, OpenVPN offers strong security and works on a wide range of devices. It uses SSL/TLS for key exchange and offers flexibility through customisation options.
- SSTP: Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is a Windows-based protocol that uses SSL to encrypt data. It is tightly integrated with the Windows operating system and provides robust security.
- IKEv2: Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) is another protocol that, like L2TP, is often paired with IPSec for added security. It provides excellent stability and performance, especially on mobile devices.
- WireGuard: A newer VPN protocol, WireGuard is lightweight and provides strong security through modern cryptographic techniques. It is still under active development but promises to be an excellent choice for VPN connections in the future.
VPN for Individual Users
Individual users can benefit significantly from using VPN services for various purposes. Personal VPNs provide security, privacy, and unrestricted access to online content. A personal VPN typically requires installing a VPN client on your device. This software creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the VPN provider’s server.
This tunnel protects your data and ensures your identity remains anonymous. VPN providers offer a wide range of server locations to choose from. By connecting to a server in a different region or country, you can access content that is blocked or restricted in your area. This means geographically restricted websites and streaming services can be enjoyed without any hassle.
Personal VPNs are simple to set up – most VPN providers offer easy-to-use software or a dedicated VPN app for your device. Some VPN services also include additional features such as ad-blocking, malware protection, and automatic server selection for the best connection speeds. Moreover, if you are a Mac user and facing issues with Teams, then you can go through our article on how to fix Microsoft Teams not working on Mac.
VPN for Businesses

A VPN (Virtual Private Network) for businesses is essential to ensure secure and private communication between your corporate network and remote workers or multiple office locations. By utilising a business VPN, you can maintain a high level of security and privacy while providing access to the company’s resources.
A business VPN often connects your Local Area Network (LAN) to a Wide Area Network (WAN), enabling your employees to access the company’s internal resources securely over the Internet.
There are two main types of VPNs used in businesses: intranet and extranet VPNs. An intranet-based VPN is typically used to connect multiple LANs within the same organisation, while an extranet-based VPN connects a company’s LAN to another company’s network or resources.
The VPN server plays a crucial role in managing the connections, ensuring that authentication and encryption are carried out correctly. These measures protect your corporate network from any unauthorised access and maintain the privacy of the data transferred across the network. Moreover, if you want to learn about screen sharing on Zoom, you can review our article, How to share screen on Zoom.
Advantages and Limitations of VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a popular solution to enhance online privacy and security. While VPNs offer several benefits, they also have limitations. In this section, we will discuss the advantages and limitations of VPNs, focusing on factors like cost, speed, logs, geo-restrictions, IPsec tunnels, and firewalls.
Advantages
- Affordability: VPNs are cost-effective compared to other security measures. With a small monthly fee, you can access a premium VPN service that secures your connection and unlocks restricted content.
- Privacy and security: VPNs encrypt your data, making it more secure from hackers and snooping third parties. With an alternate IP address, your online activities remain private.
- Geo-restrictions: VPNs allow you to bypass geo-restrictions by connecting to a server in another country, providing access to content unavailable in your region.
- IPsec tunnels: VPNs use protocols like IPsec to create secure tunnels for your data, protecting it from interception and tampering.
- Firewalls: Some VPN services include built-in firewalls, offering an extra layer of protection from cyber threats.
Limitations
- Speed: VPNs can sometimes decrease your internet speed as your data passes through the VPN server before it reaches the final destination. However, quality VPN services take measures to minimise speed reduction.
- Logs: Some VPN providers may keep logs of your usage, raising privacy concerns. Check the logging policy of your VPN to ensure they commit to a no-logs policy.
- Geo-restrictions: Though VPNs can bypass most geo-restrictions, some websites and services can still detect and block your VPN connection.
- Compatibility: VPNs might not be compatible with all devices or operating systems, so ensure your VPN service supports your devices before subscribing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the most common VPN protocols?
There are several VPN protocols, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The most common VPN protocols include:
- OpenVPN: Known for its strong security and flexibility, OpenVPN can be used over UDP (faster) or TCP (more reliable) ports. It is widely considered the gold standard for VPNs.
- L2TP/IPsec: This protocol combines Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol (L2TP) and IPsec, providing a secure connection that is often faster than OpenVPN. However, L2TP/IPsec may be susceptible to certain types of attacks.
- PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is one of the oldest VPN protocols. While it is straightforward to set up, it offers weaker security than other protocols.
- IKEv2: Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) offers robust security and excellent connection stability, making it suitable for mobile VPNs. It is often paired with IPsec for increased security.
Q2. How does a Site-to-Site VPN differ from other types?
A Site-to-Site VPN connects two or more network locations, often using dedicated hardware devices known as VPN gateways. This type of VPN differs from other types in the following ways:
- Purpose: Site-to-Site VPNs are designed to securely connect entire networks, while other VPN types generally focus on connecting individual users or devices.
- Configuration: Site-to-Site VPNs require more complex configurations involving multiple networks, routers and VPN devices.
- Hardware: Site-to-Site VPNs often use dedicated VPN gateway appliances, while other VPN types rely on software clients installed on users’ devices.
Q3. How do VPN types vary in terms of security and speed?
The security and speed of a VPN can vary significantly depending on the type and protocol used:
- OpenVPN offers a high degree of security and is highly configurable, but it can be slower than other protocols.
- L2TP/IPsec provides a good balance between security and speed, though it may not be suitable for high-risk use cases.
- PPTP is fast and easy to set up but has weaker security, making it less suitable for sensitive information or high-stakes use cases.
- IKEv2 offers robust security and excellent connection stability, especially for mobile users who frequently switch between networks.
Q4. What factors should I consider when choosing a VPN?
When choosing a VPN, consider the following factors:
- Security: Evaluate the security features and protocols the VPN offers, selecting one that provides the protection you require.
- Speed: Look for a VPN with consistent, fast connection speeds to ensure a smooth online experience.
- Compatibility: Ensure the VPN is compatible with your devices and operating systems.
- Server locations: Choose a VPN with a wide range of server locations if you need access to geo-restricted content or want to improve connection speeds by connecting to nearby servers.
- Ease of use: Opt for a VPN with an intuitive interface and user-friendly features, especially if you are new to VPNs.
- Price: Consider the cost of the VPN service and whether it offers a free trial or money-back guarantee, so you can test the service before committing.
- Customer support: Look for a VPN with responsive, helpful customer support if you require assistance.
Conclusion
In today’s digital age, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have emerged as a paramount tool for ensuring robust online security. The diverse array of VPN types cater to varying needs, from businesses looking to connect multiple locations securely to individuals aiming to maintain privacy or bypass geo-restrictions.
Furthermore, the benefits and constraints of VPNs are judiciously balanced, providing potential users with a holistic understanding of what to expect. To thrive in the digital realm and make informed decisions, comprehending the nuances of VPN types and their applications is indispensable.