Remote Desktop Port aims to be your bridge to this intricate world. Whether it’s telecommuting, managing a global server network, or aiding a friend across continents. The role of remote desktop connections is pivotal. Well, this article is designed to offer a blend of expert insights, practical advice, and technological know-how to elevate your remote desktop experiences. Let’s Solve the mystery of remote connections and step into a universe of convenience and control.
What is Remote Desktop Protocol?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a secure network communications protocol developed by Microsoft. This protocol enables you to access and control other computers remotely, providing the same functionality as operating them locally. RDP suits many network topologies and LAN protocols such as ISDN, POTS, IPX, NetBIOS, and TCP/IP.
To use RDP, you’ll need specialized remote desktop software, which commonly uses other protocols like Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) and Virtual Network Computing (VNC). However, RDP is the most widely used protocol due to its robust features and reliability.
Setting Up Remote Desktop on Windows 10
To start setting up Remote Desktop on your Windows 10 PC, you’ll first need to enable this feature. Follow these steps to allow connections:
- Open Settings by clicking on the Start button and selecting the gear icon.
- Click on System and then select Remote Desktop from the left-hand menu.
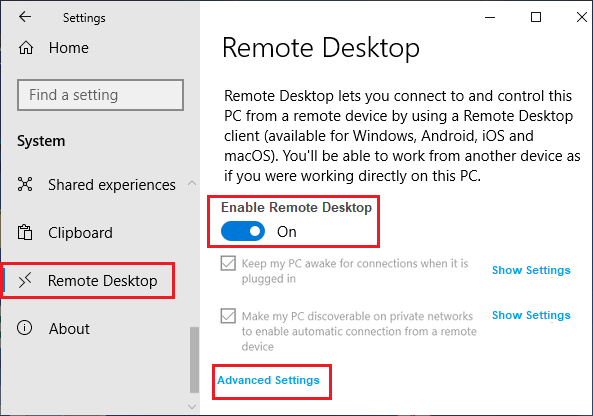
- Toggle the switch to On under the Enable Remote Desktop section. A confirmation message will appear; click Confirm to proceed.
For added security, To enable NLA:
- Go back to the Remote Desktop settings page in Settings.
- Check the box next to Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication.
Various tools for remote assistance on Windows 10, such as Remote Assistance Windows 10 Guide, offer a more in-depth exploration of features and security settings. This guide is helpful when fine-tuning your remote desktop settings.
How To Change Remote Desktop Port?
You can use either the Registry Editor or PowerShell to change the Remote Desktop Port (RDP) on your Windows system. Here are the steps for both methods:
Method 1: Using the Registry Editor
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box.
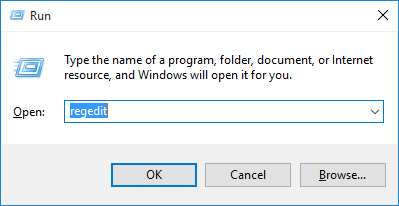
- Type regedit and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp.
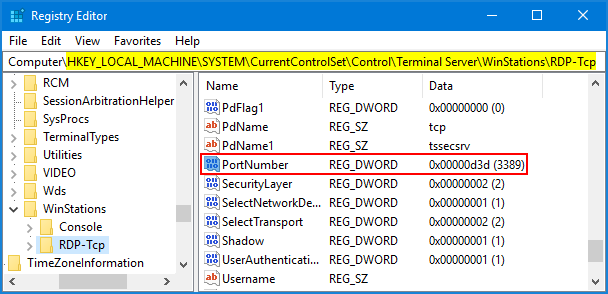
- In the right pane, find the PortNumber field and double-click it.
- Select the “Decimal” option, enter the new port number, and click “OK” to save the changes.
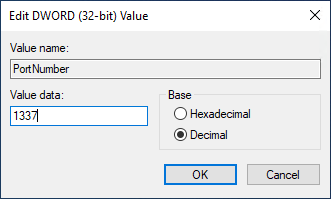
- Close the Registry Editor and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Remember to configure your firewall to allow connections on the new port number.
Method 2: Using PowerShell
1. Right-click the Start button and select “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” to open PowerShell with administrative privileges.
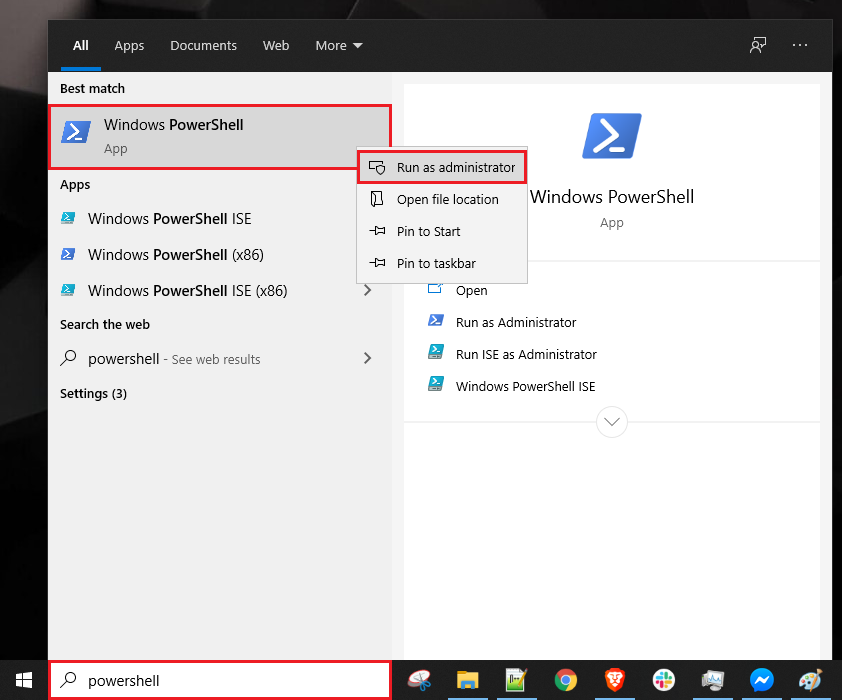
2. Run the following command, replacing NewPortNumber with the desired port number:
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -Name "PortNumber" -Value NewPortNumber
3. Close PowerShell and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Again, remember to configure your firewall to allow connections on the new port number..
How To Change Remote Desktop Port On Mac?
To use a remote desktop connection on your Mac, follow these steps:
- Download the Microsoft Remote Desktop client from Mac App Store.
- Enable remote connections on the PC.
- Open the app on your Mac, and click on the “+” button in the top right corner
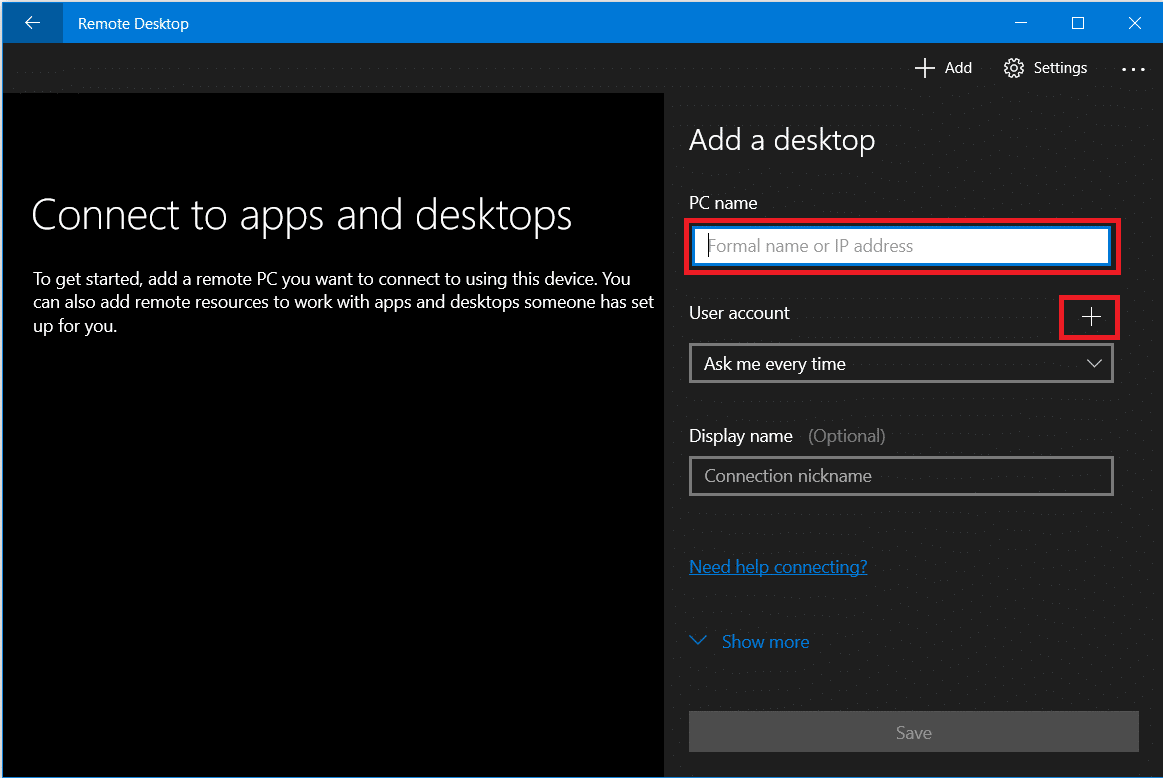
- Enter the necessary information, such as the PC’s hostname or IP address, username, and password.
- Select the added connection, and click on the gear icon to access locations.
- Here, you can adjust display settings, configure how your local devices interact with the remote PC, and more.
- Once your connection is set up, double-click on it to initiate the connection.
Remember that Apple Remote Desktop is a separate solution for managing other Macs remotely, which uses different ports (such as TCP port 5900 for control and observation functions). You can follow the Apple Remote Desktop User Guide to explore this option.
Firewall and Security Measures
When setting up Remote Desktop Services (RDS), it’s crucial to implement proper firewall and security measures to protect your network. For example, you can set and control Ubuntu Remote Desktop from Windows with ease. Here are some key points to consider:
- Configure your Firewall: Ensure your firewall has rules allowing RDS connections. You can do this by checking for rules labeled as “Remote Desktop” or “Terminal Services.”
- Change the Default RDP Port: To secure your RDS setup further, consider changing the default port that Remote Desktop listens on.
- Enable Network Level Authentication (NLA): NLA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to authenticate before establishing a connection.
- Restrict Access to RDS Port: Limiting access to the Remote Desktop port to specific trusted IP addresses or allowing connections only from certain trusted hosts can enhance security.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): Establishing a VPN connection when accessing your network remotely provides an additional layer of security.
Port Forwarding and Network Configurations
To enable remote desktop access outside your local area network, you must configure port forwarding on your router. Port forwarding allows incoming connection requests to go directly to the intended device, overcoming the router’s limitation of not allowing incoming network requests.
- Identify the Port: Remote Desktop uses TCP and UDP port 3389 by default. However, you may change the listening port as needed for security reasons.
- Configure the Router: Log in to your router’s administration panel and enable port forwarding for the Remote Desktop port (TCP and UDP 3389).
- Firewall Settings: Ensure your firewall allows inbound connections to the Remote Desktop port, permitting connections to the new port number.
- Use a VPN: To enhance security, consider using a virtual private network (VPN) to access your computer remotely.
- Public IP address: When connecting remotely, you must know your home network’s public IP address. This address may change frequently, depending on your internet service provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the default RDP port for Windows?
The default Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) port for Windows is TCP port 3389. Additionally, opening UDP port 3389 can help improve performance for RDP 8.0 and later versions.
Q2. How do I change the RDP port on Windows 10?
To change the RDP port on Windows 10, you’ll need to modify the registry:
- Open the Registry Editor by pressing Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp.
- Find the PortNumber registry entry and double-click it to change the value.
- Choose the Decimal base and enter the new port number. Click OK.
Q3. Can I use Chrome Remote Desktop without port forwarding?
Yes, you can use Chrome Remote Desktop without port forwarding. Chrome Remote Desktop uses a secure, encrypted connection that doesn’t require any additional configuration on your router.
Q4. Do I need to open port 3389 for Remote Desktop Protocol?
To use Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) effectively, you need to open port 3389 on your router for both TCP and UDP traffic. This allows remote connections to your computer using RDP. However, you should also consider other security measures, such as using a VPN or setting up port forwarding correctly, to ensure your connection is secure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Remote Desktop Protocol is crucial for effectively managing and accessing remote computers. By building your knowledge of RDP, you can confidently perform tasks on remote systems and ensure a secure and efficient workflow. Remote desktop technology allows you to connect to and control your computer from another location with ease. Utilising this technology can improve your ability to work remotely, offer support to users, or access resources on your home or office network from anywhere.