Remote Desktop Services (RDS) and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) are two critical technologies for remote access. While they often serve similar purposes, they differ significantly in functionality and application. RDS is a server-based platform that enables access to virtual desktops and applications for multiple users, known for its efficiency and scalability. RDP, a part of the RDS suite, is a Microsoft protocol focused on individual connections using a graphical interface.
Understanding the nuances of RDS vs RDP is crucial for IT professionals and organizations seeking to implement a robust remote access solution. The choice between these two can impact various aspects such as cost, performance, security, and scalability. In this insightful comparison, we will delve into the specific characteristics of RDS and RDP, offering a comprehensive understanding of their benefits, limitations, and best-use scenarios. Thus empowering you to make an informed decision tailored to your unique needs.
Understanding RDS vs RDP
Two technologies often come to mind for remote desktop solutions: Remote Desktop Services (RDS) and the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). RDS is a feature of the Windows Server, providing users access to applications, data, and Remote Desktop Services Host desktops. On the other hand, RDP is a network communication protocol developed by Microsoft to connect to another computer over a network.
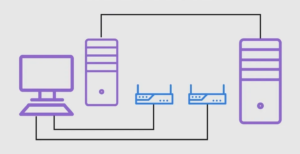
To understand the difference between RDS and RDP, it is crucial to know how they work. With RDS, a server runs multiple instances of the Windows operating system, each dedicated to one user. This means that users can access applications, data, and even entire desktops remotely as if using their local computers. It is constructive for businesses that use multiple applications and need to centralize resources and software.
What is RDP?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary technology developed by Microsoft that allows you to connect to another computer over a network. When using RDP, you can control the remote computer’s operating system (OS) and applications as if you were physically present. RDP is essential for many remote desktop solutions, such as Remote Desktop Services (RDS), as it transmits commands and graphical user interface data between the server and the client.
What are the uses of RDP?
RDP technology has various applications, such as enabling remote access to your Windows-based personal computer at work or accessing virtual desktops in a cloud-based environment. Companies can deploy RDP to manage IT infrastructure and troubleshoot issues remotely. At the same time, end users can utilize it for seamless access to applications, data, and resources without being limited by physical location.

Benefits
The benefits of using RDP are numerous and include:
- Flexibility: RDP allows you to access your Windows desktop and applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Increased productivity: Users can work on projects and access required resources without travel or time limitations.
- Reduced downtime: IT staff can address and resolve technical issues quickly and efficiently without physically visiting the affected machines.
- Centralized management: Administrators can monitor the entire Windows infrastructure from a single location.
- Business continuity: RDP can provide uninterrupted access to applications and data, even in cases of hardware failures, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events.
By leveraging RDP, you can ensure seamless access to your resources and benefit from increased productivity, flexibility, and centralized management while minimizing downtime and maintaining business continuity. Remember to follow a Microsoft Remote Desktop Mac guide to connect to Windows PCs and virtual desktops from your Mac device.
What is RDS?
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a technology that allows you to initiate and control an interactive session on a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. This Microsoft Windows feature helps set up a centralized and organized environment to provide remote access to graphical desktops and Windows applications, such as Microsoft Remote Desktop.
What are the uses of RDS?
While RDS relies on the Windows Server operating system, RDP is the underlying technology that enables remote connections between the server and the client. RDP transmits commands and graphical user interface (GUI) elements between the server and the client. It is worth mentioning that the Remote Desktop functionality is also available on non-server Windows operating systems, such as Windows 10 Professional.

Benefits
- Access to Windows Server: RDS enables you to connect and work with a Windows server from any device with an internet connection. Your work is centralized, allowing greater collaboration among team members.
- RemoteApp deployment: By utilizing RDS, you can deploy applications remotely. Your employees can access specific applications without gaining full rights to the server environment. This offers simplicity and security.
- Scalability: With RDS, you can quickly and easily add new users and resources without purchasing additional hardware.
Remember that using RDS effectively can enhance productivity, enable collaboration, and maintain a secure, organized workspace.
Head on Head Comparison: RDS vs RDP
While both RDS vs RDP offers a range of features to enhance remote access, RDS tends to provide a more robust and seamless experience due to its centralized management, device support, and added security features. When evaluating the best option for your needs, consider each solution’s full spectrum of advanced features.
Security Aspects
RDS, a part of the Windows Server family, provides a more secure environment than RDP. It uses the Microsoft Remote Desktop Services gateway, which employs Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt communications and prevent the system hosting the remote desktop from being directly exposed to the public internet.
Conversely, RDP is the underlying protocol that powers remote desktop connections on Windows computers. Although it provides basic security features, such as encrypted channels and support for smart card authentication, it may carry some security risks.
Functionality and User Interface
Remote Desktop Services and Remote Desktop Protocol or RDS vs RDP play vital roles in remote desktop solutions. You might have encountered both terms. Both options offer value, but the choice between RDP and RDS depends on your requirements and desired user experience. Regarding functionality, RDP is a protocol developed by Microsoft that enables remote access and control of a computer from another device.
RDS is a set of functionalities built on top of RDP. It allows multiple users to access and use a Windows server simultaneously. Using RDS, you can create a centralized workspace where users can run applications, manage files, and perform other tasks without requiring individual computers.
Virtualization and Cloud Aspects
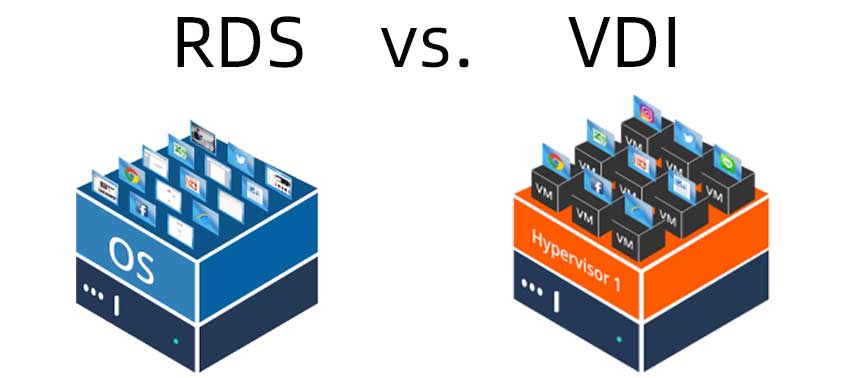
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and Remote Desktop Services (RDS) are leading remote desktop solutions that leverage virtualization and cloud technologies. VDI hosts a personalized virtual desktop on a centralized server like Microsoft Azure, allowing seamless access from any device.
It offers efficient resource usage and significant customization options. Conversely, RDS (or Remote Desktop Protocol) provides access to a centrally managed server with more limited customization. While VDI creates unique settings for each user, RDS presents a standardized virtual environment. The choice between VDI and RDS hinges on specific requirements, with cloud technologies like Azure enhancing efficiency.
Server and Hardware Considerations
When deploying Remote Desktop Services (RDS) or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), several key considerations must be considered for optimal performance. Storage requirements, including IOPS and capacity, must align with user data and application needs. CPU and memory resources should be matched to the number of users and complexity of applications.
Server location minimizes latency and improves connectivity, while load balancing ensures efficient traffic distribution. Selecting the proper hardware for terminal servers, considering workloads and security, can optimize performance. A thoughtful approach to these hardware and server factors ensures a responsive and scalable RDS vs RDP environment capable of providing a seamless user experience.
RDS vs RDP: Advanced Features Comparison

When comparing RDS vs RDP, it’s essential to understand the advanced features they offer. Both solutions provide remote access capabilities.
1. Authentication
Regarding user authentication, RDS enables you to manage users centrally through the domain, streamlining the sign-in process. With RDP, you must provide your username and password whenever you connect to a remote machine or service.
2. Hardware
For peripherals and hardware, RDS supports various devices, including USB peripherals, cameras, and printers. You can configure RDS to allow redirection of these devices, ensuring a seamless experience when working remotely. In contrast, RDP offers limited device support, and connecting hardware can become cumbersome.
3. Input Devices
When it comes to keyboard and input devices, both RDS vs RDP support various keyboard layouts and input methods. However, RDS provides better keyboard synchronization, ensuring your local keyboard layout matches the remote machine.
4. Clipboard
Clipboard functionality is essential for any remote access tool, and both RDS and RDP include clipboard support. This feature allows you to copy and paste text, images, and files between your local machine and the remote system.
5. Printing
In the context of remote printing, RDS offers comprehensive printer redirection, enabling you to print documents from the remote machine to your local printer. RDP can also support printer redirection but may require additional configuration and driver installation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the main differences between RDS and RDP?
Remote Desktop Services and Remote Desktop Protocol or RDS vs RDP are both related to remote access. RDS is a server-based technology that provides a scalable and multi-user environment for hosting applications. RDP is a communication protocol created by Microsoft for remote connections between clients and servers. In short, RDS uses the RDP protocol to provide a centralized, multi-user computing environment.
Q2. What is the purpose of Microsoft’s RDS?
Microsoft’s RDS (Remote Desktop Services) is designed to provide a scalable, multi-user computing environment that allows users to access applications, data, and even entire desktop sessions on a remote server.:
- Improved security: RDS helps reduce the risk of data leakage and unauthorized access by keeping sensitive data and applications on a centralized server.
- Simplified management: IT administrators can manage applications, software updates, and user permissions all from a single location, cutting down on time and effort.
- Cost savings: By consolidating hardware and software resources, organizations can reduce IT overhead and save on hardware, energy, and maintenance costs.
- Accessibility: Users can access their work environment from any device, improving flexibility and mobility for remote or traveling employees.
Q3. What are the key features of RDP?
- High-quality audio and video streaming: RDP supports high-quality audio and video streaming, providing a seamless user experience during remote sessions.
- Multi-monitor support: Users can work with multiple monitors during a remote session, improving productivity and workflow.
- Clipboard sharing: RDP allows users to share their clipboard between the local and remote devices, making copying and pasting content between them easy.
- Smart card authentication: RDP supports smart card authentication, adding an extra layer of security when connecting to remote devices.
- Printer redirection: RDP lets users print documents from the remote device to their local printer, streamlining the printing process.