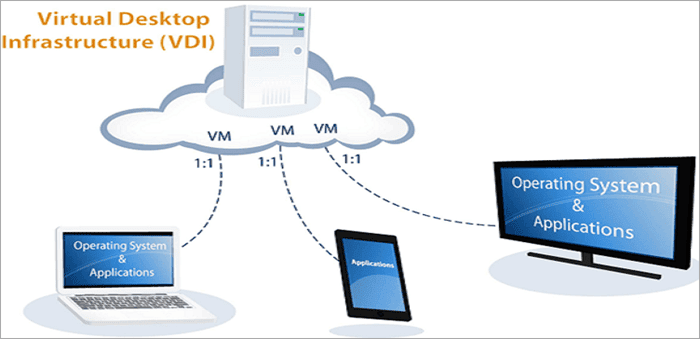
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) has become an essential component of modern IT infrastructure, offering numerous advantages for businesses and organizations needing centralized management and remote access capabilities. VDI refers to hosting desktop environments on a central server, allowing these environments to be provided and managed using virtual machines.
But since it is a new technology, not many people know about it. That’s why we are here to help you. In this article, we will tell you what is a VDI and its fundamentals. Along with this, you will also get to know about its applications, key components, future, and how this technology is impacting other industries. So now, let’s get started.
What is a VDI? (Fundamentals of VDI)

Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is growing rapidly because of its ability to streamline, centralize, and simplify desktop management. By hosting desktop environments on a central server, it allows organizations to deliver virtual desktops to users on various devices, like PCs, tablets, and even smartphones. In this section, we’ll explore the fundamental concepts behind VDI and compare virtual desktops to physical PCs from a management and user perspective.
- Virtual Desktops Versus Physical PCs
One of the key differences between virtual desktops and physical PCs is how they are hosted and managed. In a VDI environment, desktop environments run on virtual machines that are hosted on a centralized server.
This enables organizations to efficiently deploy, update, and maintain desktop environments for users. In contrast, physical PCs require manual and individual management, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Types of VDI
There are two main types of VDI: persistent and non-persistent VDI. In a persistent VDI setup, virtual desktops are tailored to individual users, each receiving a dedicated and personalized environment. This type of VDI is ideal for organizations that require customization for different users.
Non-persistent VDI, on the other hand, provides a standard and consistent virtual desktop environment for users. Each time users log in, they access a “fresh” desktop environment that resets upon logout. This setup suits organizations that prefer uniformity and limited user customization.
- User Access
VDI enables users to access their virtual desktops through a thin client, a minimalistic device designed only to connect to a network for VDI access. With a thin client setup, users can securely connect to their virtual desktops from anywhere, providing greater flexibility and mobility.
Applications of VDI
VDI allows users to access their desktops from any device, offering a secure and consistent experience. This technology has helped various industries and sectors, significantly affecting remote work, remote desktop services, and application virtualization. Now that you know what is a VDI, here we will discuss several applications of VDI and its impact on modern work environments.
1. Enabling Remote Work
With the rise of the gig economy and the recent shift towards remote work due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for secure and flexible working solutions has become paramount. VDI allows employees to access their work desktops from any device, enhancing productivity and providing a seamless user experience. This flexibility is ideal for companies with distributed teams and employees.
2. Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
VDI hosts desktop environments on a centralized server and deploys them to end-users on request, providing a smooth and consistent experience across devices. For example, Microsoft offers the Windows Virtual Desktop service, which integrates with Azure Virtual Desktop, allowing businesses to deploy and scale virtual desktops on-demand easily.
3. Desktop Virtualization
By hosting the desktop environments within virtual machines (VMs) on a central server, VDI allows for isolating individual users’ environments. This setup ensures data security and makes it easier for IT administrators to manage and maintain the systems. Additionally, virtualized desktops can run on various platforms, allowing organizations to extend their computing infrastructure.
4. Application Virtualization
Application virtualization with VDI offers many advantages, including centralized management, simplified updates, and increased security. Companies like Citrix have developed solutions such as Citrix Virtual Apps and Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops.
They take advantage of VDI to deliver applications and desktop environments securely. These solutions streamline application deployment, reduce costs, and improve user experience across diverse devices and locations.
VDI & Different Industries (What is a VDI and Its Impact on Different Industries)

VDI provides a flexible and scalable solution for various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, education, retail, and federal. After knowing what is a VDI, here we will explore the benefits and applications of VDI in these industries, emphasizing its impact on productivity, security, and cost-effectiveness.
VDI in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, VDI plays a crucial role in streamlining patient care and ensuring data security. By centralizing medical records and applications, healthcare providers can access patient information more efficiently, leading to timely and accurate diagnoses. Moreover, VDI helps maintain robust security measures and data encryption.
Some advantages of VDI in healthcare include:
- Enhanced patient experience through coordinated care and faster medical services
- Minimized data breaches due to advanced security and encryption features
- Improved productivity with remote access to clinical applications and records
- Reduced IT expenditures through efficient hardware and software management
VDI in Education
VDI simplifies IT management, encourages collaboration, and provides equal access to resources across campuses. By standardizing the educational platform through VDI, students, and faculty can access the same software, applications, and digital resources regardless of their location or device.
Key benefits of VDI in education are:
- Expanded access to learning materials and applications for remote students
- Enhanced collaboration and interaction among students and teachers
- Simplified IT management, maintenance, and updates, reducing administrative workload
- Increased data protection and privacy for student and institutional information
Moreover, if you are a student and you want to learn how to sceen share on Zoom, then you can check out our article,
VDI in Retail
VDI has significant implications for the retail industry, as it streamlines operations, enhances customer experiences, and supports seamless inventory management. Equipping retail employees with virtual desktops delivers real-time sales data, price changes, and inventory information, which enables them to assist customers better and make informed decisions.
In retail, VDI offers:
- Improved customer service through real-time access to sales, pricing, and inventory information
- Enhanced productivity by reducing device downtime and maintenance costs
- Increased data security for POS systems and sensitive customer data
- Flexible workforce management and support for seasonal employees
VDI in Manufacturing
VDI plays a significant role in this digital transformation. Virtual desktops provide access to critical applications like Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, enabling workers to collaborate and improve productivity seamlessly. Additionally, VDI supports remote access to these systems, allowing off-site engineers and designers to contribute effectively.
VDI benefits in manufacturing include:
- Streamlined collaboration and data sharing across departments and remote workers
- Enhanced security for intellectual property and sensitive information
- Support for Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, reducing hardware costs
- Simplified IT management, with centralized updates and maintenance
Along with this, remote IoT applications are also helping various industries in improving their functioning.
Key Components of VDI

VDI provides an isolated environment for each user and delivers the same user experience as a traditional physical desktop. Now that you know what is a VDI, here we will discuss the key components of VDI.
1. Hypervisor
A hypervisor is a software layer that allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical host. It is one of the most important concepts of what is a VDI. This technology is crucial for VDI, as it enables organizations to segment servers into VMs that, in turn, host virtual desktops.
2. Operating System
The operating system is typically a desktop operating system such as Microsoft Windows, which is installed on virtual machines, allowing users to access and manage their desktops remotely. Some popular operating systems used in VDI solutions are Windows 10, macOS, and Linux distributions.
3. Management Services
These services are responsible for managing and delivering virtual desktops to end-users. They help to allocate resources, monitor performance, maintain security, and update the desktops when necessary. It also ensures that virtual desktops are highly available and meet the desired performance standards.
4. Display Protocol
Another important component of what is a VDI is display protocol. They are responsible for transferring the user’s input, such as keyboard and mouse events, to the virtual desktop and providing the user with graphical output. Display protocols should be optimized for high-quality visuals and low latency to ensure a responsive user experience.
5. Data center infrastructure
A data center provides the physical resources, including computing, storage, and networking, required to host virtual machines that run virtual desktops. Organizations can choose between on-premises data centers or use cloud-based services such as Microsoft Azure or Amazon Web Services (AWS) to host their VDI.
6. Server virtualization
This vital component of what is a VDI enables organizations to run multiple virtual desktops on a single physical server. This virtualization helps to maximize resource utilization and improves the overall efficiency of the infrastructure.
Future of VDI Technology
After knowing what is a VDI, let’s dive in and have a look at the future of VDI. As demands for increased scalability, flexibility, and device compatibility rise, the future of VDI technology promises to address these challenges while providing a seamless user experience across a wide range of devices and platforms.
As VDI continues to gain traction, we can expect it to support the expanding range of devices, making it easier for users to access their applications and data across different platforms.
The growth of cloud computing services like Microsoft Azure is another driving force in the development of VDI technology. With the rise of cloud-based solutions, organizations can now deploy and manage their VDI infrastructure in the cloud, which offers several benefits, such as improved scalability, cost-efficiency, and agility.
Integrating VDI with cloud services allows for more significant expansion as demand increases, and it also reduces the total cost of ownership for organizations, making the technology increasingly attractive and affordable.
In parallel, advances in VDI technology are enhancing its capabilities to handle more complex and resource-intensive tasks. As the technology continues to improve, it is expected to handle even more demanding workloads without compromising performance.
We can also anticipate greater integration of VDI with Windows and other popular operating systems. This will streamline the user experience and improve the overall efficiency and productivity of organizations utilizing VDI technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are some popular VDI platforms?
Some of the most widely-known VDI platforms include Microsoft Azure, VMware Horizon, Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, and Amazon WorkSpaces.
These platforms vary in their features, pricing, and supported platforms. It’s essential to research each platform and compare them to the specific needs of your organization to identify the most suitable option.
Q2. How does VDI compare to traditional desktop environments?
In a traditional desktop environment, users work directly on the hardware of their computers, and all of their data and applications are installed locally on the device. On the other hand, VDI runs a user’s desktop on a virtual machine located in a data centre, with all applications, operating systems, and settings managed centrally. This centralization allows IT staff to manage all virtual desktops more efficiently and make updates, patches, and other management tasks easier and faster.
Q3. What are the benefits of using VDI?
Implementing VDI offers several notable benefits to organizations:
- Easier management: It allows managing all virtual desktops centrally, streamlining the update process, application deployment, and other administrative tasks.
- Improved data security: Because VDI stores user data and applications in a centralized data center, there’s a reduced risk of data breaches.
- Increased accessibility: VDI allows users to access their desktop environment from any device with an internet connection, enabling them to work remotely or use their preferred device more easily.
- Cost-effectiveness: VDI often lowers the hardware cost since virtual desktops require fewer resources than traditional desktops. Moreover, VDI makes it easier to scale up or down the number of desktops based on the organization’s needs.
- Better performance: It delivers better performance and user experience, even on less powerful devices like thin clients or older PCs.
Q4. What is the difference between VDI and Remote Desktop Services?
While VDI and Remote Desktop Services (RDS) both enable users to access a desktop environment remotely, there are key differences between the two solutions.
VDI provides each user with a separate virtual machine running a complete desktop environment, including the operating system and applications. This individualized approach allows for more customization and personalization of the user’s workspace.
In contrast, RDS (formerly known as Terminal Services) relies on a shared server operating system to host multiple user sessions simultaneously, with each user sharing the same underlying resources and applications.