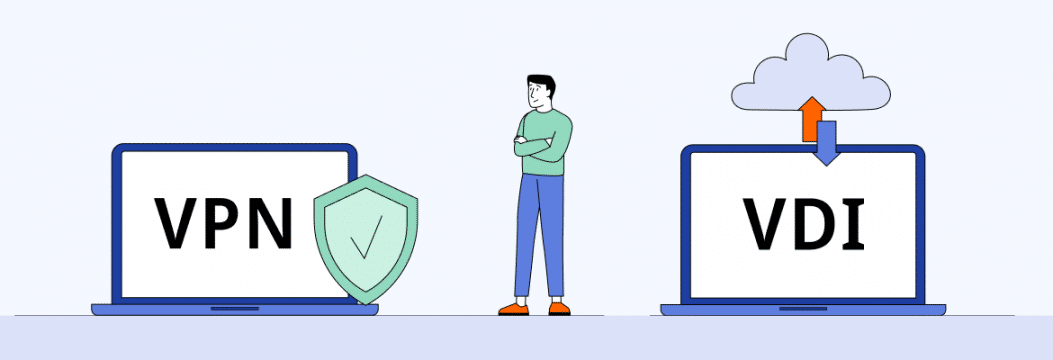
Ever wondered which path to take for remote access? In the vast realm of digital workspaces, two giants cast long shadows: VPN and VDI. They are not just the buzzwords of the tech world but the cornerstone of secure, remote accessibility.
One is creating encrypted tunnels, and the other is crafting entire digital universes accessible from a humble screen. Hence, the debate emerges VPN vs VDI? As you grapple with the choice of VPN or VDI, we’re here to light your way. Dive into this comparison as we unravel their mysteries, strengths, and challenges, guiding you to the perfect choice for your organization’s unique narrative.
What is a VPN?
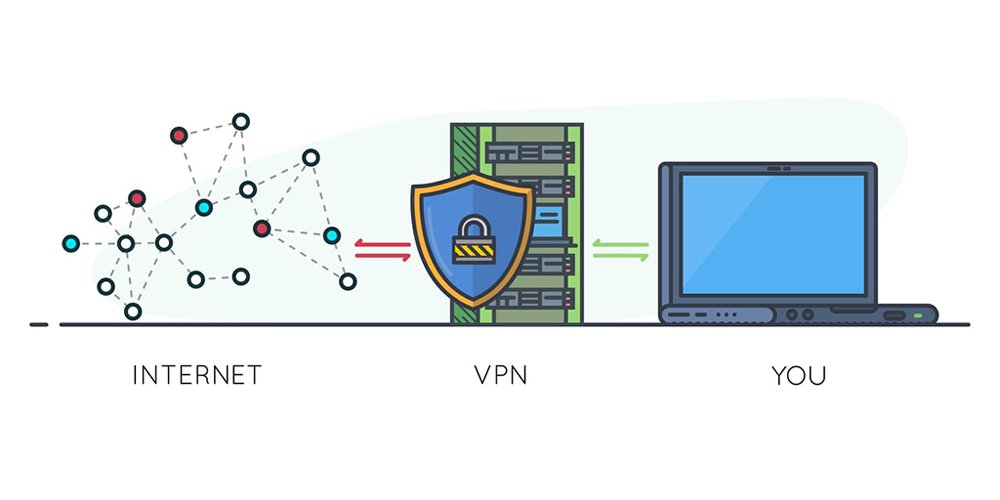
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that enables you to create a secure tunnel between your device and a VPN server. This secure connection helps protect your internet connection by encrypting the data transmitted between your device and the VPN server, ensuring privacy and security. If you are looking for popular VPN services, then you can check Nord VPN and Express VPN.
Mechanism
When using a VPN, your IP address is hidden, and your internet traffic is rerouted through the VPN server. This not only masks your true IP address but can also make it appear as if you are accessing the internet from a different location. One primary use for a VPN is to provide secure remote access to resources on a private network, such as your office network or a university campus.
Advantages
- Protection: This helps protect your data from being intercepted or tampered with by hackers, government surveillance, or other third parties who may want to access your information.
- Remote Access: A Remote Access VPN connects individual users to a private network. This type of VPN can decrypt your data, check the destination, and encrypt it again to send it off securely.
- Great Flexibility: Because of this encryption and secure tunneling, VPNs are often used by businesses and organizations to ensure that employees can securely access company resources while working remotely.
What is a VDI?
A Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that allows you to access a fully functional desktop environment remotely. It creates virtual machines that host their own operating systems, applications, and data. These virtual desktops are then accessed by users from various devices, which act as thin clients.
Mechanism
In a VDI setup, virtual desktops are run on a central server and are accessible from any device with an internet connection. This provides users with the flexibility to work with their desktop environments from anywhere. One of the main components of VDI is the golden image. This image contains the operating system, applications, and configuration settings needed to construct individual virtual desktops. You can check top VDI, such as Citrix’s official pages and VMware to get into it.
Advantages
- Enhanced security: Since the data and applications are stored on a central server, there is a reduced risk of data breaches due to lost or stolen devices.
- Easy management: Administrators can manage and maintain virtual machines more efficiently by simply updating the golden image.
- Improved resource utilization: Virtual desktops can share resources, such as CPU and memory, which leads to more efficient usage of hardware resources.
- Cost savings: Organizations can save on hardware costs using thin clients instead of traditional desktop computers.
When To Use: VPN vs VDI
When it comes to applications for remote work, both VPN and VDI offer a means of accessing off-site resources and providing secure remote access to users. In this section, we’ll discuss the various applications of VPN and VDI for remote work, user experience, and remote access to internet resources.
VPN Applications
A VPN enables you to establish a secure, encrypted connection between your remote device and a private network. Some key applications of a VPN include:
- Remote access to corporate networks: VPNs allow remote users to access their company’s internal resources, such as shared folders and internal applications, as though they were physically connected to the network.
- Secure browsing over public Wi-Fi: By routing your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel, VPNs protect your browsing data from potential eavesdroppers on public networks.
- Bypassing geographic restrictions: VPNs can help you access geo-restricted content by allowing you to connect to a server in a different country, making it appear as if you’re browsing from that location.
VDI Applications
VDI allows you to deliver a virtual desktop environment to remote users, enabling them to access and use applications and resources on a centralized server. Some key applications of VDI include:
- Centralized management: VDI simplifies IT management by centralizing desktops in one location, making it easier to deploy updates, patches, and new applications.
- Resource scalability: VDI makes it easy to scale resources according to the needs of your remote users, facilitating an efficient allocation of resources based on individual requirements.
- Consistent user experience: With VDI, remote users can access their virtual desktops from any device, providing a consistent and familiar user experience, regardless of where they are working from.
Factor Based Comparison: VPN vs VDI

1. VPN vs VDI: Performance and Speed
When evaluating the performance and speed of VPN and VDI solutions, there are several factors to consider, including connection speed, latency, bandwidth, and potential bandwidth bottlenecks.
| Factors | Who is Strong? VPN vs VDI |
| Connection Speed | VDI offers a consistently fast experience |
| Latency | VDI has a lower latency |
| Bandwidth | VDI consumes less bandwidth |
VDI tends to deliver better performance and speed in terms of connection, latency, and bandwidth management as compared to VPN. However, choosing these two technologies depends on your specific use case and requirements. Let’s check how:
Connection Speed
The connection speed of a VPN depends on various factors, such as the user’s internet connection, distance to the VPN server, and server load. Typically, VPNs can cause a slight decrease in connection speed. In contrast, VDI offers a consistently fast experience, as the data and applications are hosted on a central server, eliminating any speed-related issues. However, if you are working from home and looking for VPN then you must check this guide to know more about VPN.
Latency
Latency refers to the delay between a signal being sent and received in a network. In general, VDI has lower latency. Users only need to send keyboard and mouse input data, along with receiving screen updates, resulting in reduced network latency. On the other hand, VPNs can experience higher latency due to the additional hop through the VPN server and the encryption overhead.
Bandwidth
VDI solutions consume less bandwidth than VPNs, as they only need to transmit image-based data rather than the entire application data. This efficiency can also help with reducing bandwidth bottlenecks and improving network performance. VPNs transfer all the data required for remote applications, which can lead to increased bandwidth usage.
2. VPN vs VDI: Security Measures

When it comes to security measures, both VPN and VDI have their strengths. Understanding their unique benefits and limitations will help you make an informed decision about which solution is best for your organization.
VPN
With a VPN, your employees connect to the corporate network through a secure tunnel, which encrypts user data and allows only authenticated users to access confidential data. VPNs have evolved to include features like multifactor authentication and data encryption, which provide additional layers of security. Well, there are so many types of VPN as well, you can check our guide to know which would suit you best.
VDI
On the other hand, VDI provides self-contained virtual desktop environments for remote users. Here, all processing and data storage occurs within the data center, reducing the risk of data breaches. Data security is further enhanced as end-user devices are unimportant for the overall experience, reducing the attack surface for malware and ransomware.
VPN vs VDI: Which is More Secure?
Both VPN and VDI have valuable security measures that can help protect your corporate network and safeguard your confidential data. While a VPN provides a secure connection and data encryption, it may be more susceptible to malware and ransomware attacks, whereas VDI benefits from centralized data storage and reduced exposure to these threats.
3. VPN vs VDI: Management and Maintenance

When it comes to the management and maintenance of both VPN and VDI solutions, there are some key differences that you should be aware of as an IT professional.
VPN
With a VPN, the IT team is responsible for managing the VPN server and providing access to users. The VPN server requires regular updates and patching to ensure security and optimal performance. On the client side, hardware management and troubleshooting are left to the end user, as the VPN depends on client hardware.
VDI
In contrast, a VDI offers more centralized system management as it relies on dedicated resources on the server. Thus enabling IT teams to maintain and troubleshoot the environment more easily. Customization and control are also easier with a VDI, as IT teams can manage and deploy software updates, patches, and settings across multiple virtual machines. If you want to know more about VDI then you can check our guide.
VPN vs VDI: Which is easier to manage?
While both VPN and VDI solutions require management and maintenance, VDI offers more centralization and control for IT teams, making it easier to deploy updates, troubleshoot issues, and customize the user experience. On the other hand, VPNs may have lower maintenance costs but can present challenges due to their reliance on client hardware and limited control over the end user’s environment.
4. VPN vs VDI: Cost Comparison

When comparing the costs of VPN and VDI solutions, it’s essential to consider both the initial setup costs and the ongoing subscription fees. Each solution has its advantages and disadvantages regarding cost, so let’s break them down.
VPN Costs:
- A VPN typically requires a lower initial investment, making it more affordable for small businesses and individuals.
- Ongoing costs for a VPN are usually subscription-based, with many providers offering monthly or yearly plans.
- VPN connections rely on the user’s device for processing, meaning that the hardware and system updates can impact the overall experience and costs.
VDI Costs:
- VDI solutions tend to have higher initial costs as they require a more robust infrastructure setup.
- The ongoing costs of a VDI solution can be more cost-efficient in the long run, especially when deployed in a public cloud environment.
- As VDI has minimal hardware requirements, user devices have less impact on the overall experience.
Key Differences Between VPN and VDI
When deciding between a VPN (Virtual Private Network) and a VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure), it’s essential to understand the primary differences between the two technologies. Here’s a breakdown of the main distinctions to help you make an informed choice for your business:
| Features | VPN | VDI |
| Connection | Establishes a secure tunnel between your device and your private network. | Provides access to a remote virtual desktop. |
| Admin Control and Storage | VPN does not provide centralized admin control. | Offers a central point of administration. |
| User Devices | Relies on the capabilities of the user’s existing device to run applications and access resources. | Can be accessed from various endpoint devices, such as thin clients, personal devices, or even low-spec computers. |
| Performance and Graphic Processing | A VPN relies on the processing power of the end-user device. | Efficient bandwidth and latency. Good for 3D modeling or video editing |
| Security and Endpoint Device Management | VPN requires additional security measures, such as endpoint device protection software and user authentication | Administrators can enforce strict security policies and manage updates more effectively |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the main differences between VDI and VPN?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and Virtual Private Network (VPN) are two remote access technologies that serve different purposes. VDI allows you to access a virtual desktop environment hosted on a remote server. This leads to minimal hardware requirements and provides flexibility in device choice for end-users.
On the other hand, VPN is a technology that enables secure connections between your device and a remote network by creating a secure and encrypted tunnel. The main focus of VPN is to provide a more secure path for your internet traffic to travel through, whereas VDI is focused on providing users with a virtual desktop experience.
Q2. How do VDI and VPN compare in terms of security?
VDI is generally considered to be more secure than VPN as it is not directly tied to the local device and is managed centrally. This means that data remains within the data center, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data leakage. VDI also allows for more comprehensive security measures, such as single sign-on (SSO) and data encryption.
Q3. Which is better for remote access, VDI or VPN?
The choice between VDI and VPN for remote access largely depends on your specific use case and requirements. VDI is generally faster and more secure than VPN, making it a better option for environments where users need access to multiple software applications or higher security standards.